Big Data as a Service: the Next Big Thing?
Big data is large and complex unstructured data (images posted on Facebook, email, text messages, GPS signals from mobile phones, tweets, and other social media updates, etc.) that cannot be processed by traditional database tools. Big data has three dimensions: volume, velocity, and variety.
Three Dimensions of Big Data
Big Data as a service (BDaaS) is a term typically used to refer to services that offer analysis of large or complex data sets, using the cloud hosted services. Similar types of services include software as a service (SaaS) or infrastructure as a service (IaaS), where specific Big Data as a service options are used to help businesses handle what the IT world calls big data, or sophisticated aggregated data sets that provide a lot of value for today’s companies.
In general, Big Data as a service will offer various kinds of data analytics. For example, a company could use it to monitor a large SEO or Web content campaign that reaches a broad audience. In a BDaaS model, these services will commonly be offered over the Internet with key vendor storage and functionality tools located in the cloud. These setups help to provide agile services that can perform well, although businesses will not have control over many of the spaces over which their data traverses.
Experts have identified other common marketing strategies for Big Data as a service. One of these is the location of cloud data storage resources in combination with analytics, so that hot or cold data is stored near where it will be manipulated for analysis. This can help decrease the amount of effort needed to move data through an analytics program or platform. Other selling points of BDaaS include specific descriptions of how these tools can help present big data to busy managers in a cohesive and useful way, where predictive analysis companies are creating many different kinds of tools to help businesses get actionable results from data.
The ingredients necessary for BdaaS Include:
- High-Functioning Service-Oriented Architecture.
- Cloud Virtualization Capabilities.
- Complex Event-Driven Processing.
- Business Intelligence Tools.
Businesses are interested in the same functionality for their Data Management needs. Many companies lack the ability to hire a full staff of Data Scientists, but to remain competitive, they’ll need access to the same data much larger businesses have. Through Big Data as a Service (BDaaS), small to medium businesses (SMBs) can have the benefit of Big Data without the exorbitant expense of a full-time staff member.
As Data Scientists enter the field in larger numbers, many will have a choice of employers. Some of those choices will be large and mid-sized corporations, but some will be service providers. The service providers will offer data for a fee, allowing businesses from a wide variety of industries to have access to their team of data experts.
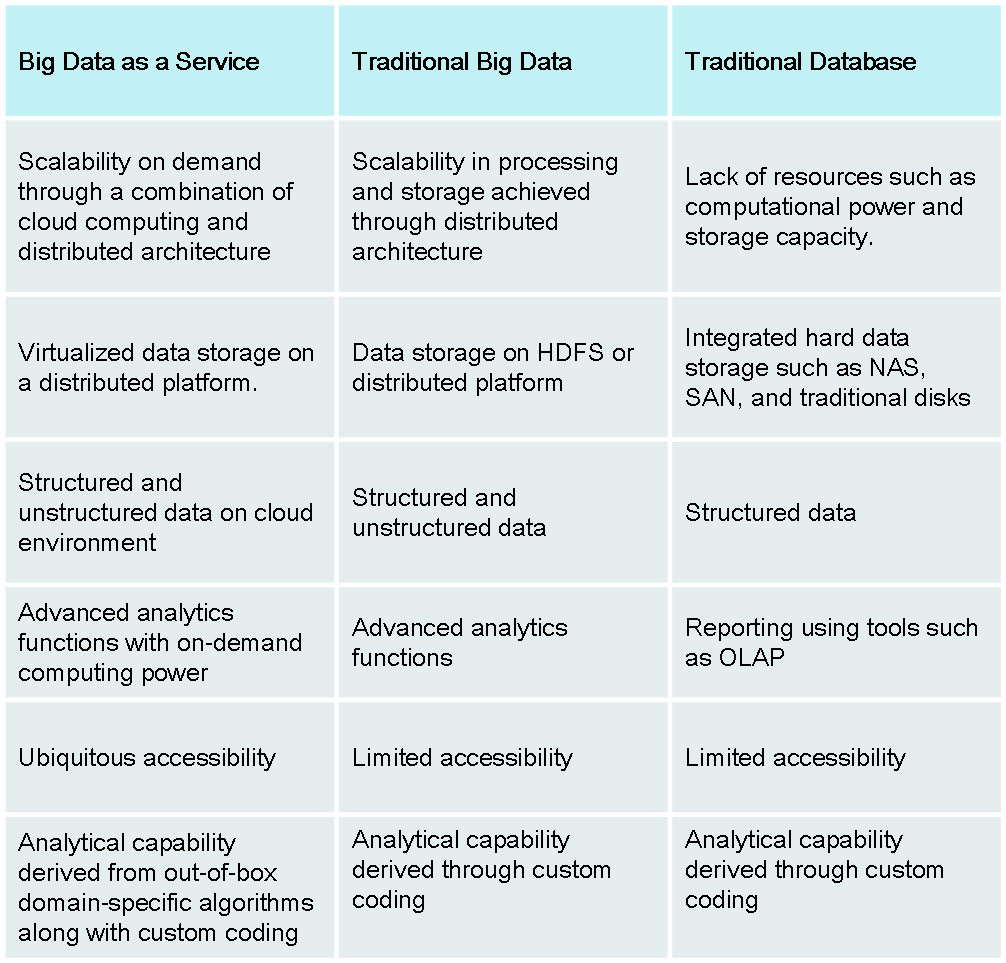
Differences between BDaaS ,Traditional Big Data and Traditional Database
Big Data as a Service Business Models
- Core BDaas :
- Performance BDaaS
- Feature BDaaS
- Integrated BDaaS
As Big Data is maturing as a topic business and service models are emerging and we can see the advantages and differences between the four competing types of Big Data as a Service. The core BDaaS has been around for a few years and is in use by many companies especially as part of a larger architecture or for irregular workloads. It has settled as a model supporting the provider’s wider service architecture.
The feature and performance BDaaS attack the segment with very different value propositions and there are good reasons for both of them to continue to attract customers. Both will have to address some features of the other in the long run. For example, the feature BDaaS needs to proof to be competitive on a performance level though the commoditization and service level abstraction means that at the end of the day not the model wins that squeezes the most performance from comparable hardware but on a dollar to dollar basis.
The performance BDaaS, will face business demands from companies that decreasingly are willing to take on the complex challenges of building their own data architecture and related SaaS layer, and increasingly want to focus on their value adding domain specific processes. So while neither of the semi-integrated BDaaS approaches want to square the circle their customer demand may yet push them to try it.
The Future
Not all industries will receive identical benefits from Big Data though. While it’s highly likely all of this data will be an increasingly important part of day-to-day business, some industries stand to benefit more than ever. Here are four industries that will likely benefit most from BdaaS: Medical Research, Financial Institutions, Retail and Government.
This text is also published in Ahmed Banafa’s LinkedIn profile
Ahmed Banafa
IoT Expert | Faculty | Author | Speaker
References
http://www.customercentric.info/is-bdaas-next-years-big-thing/
http://web.mit.edu/smadnick/www/wp/2014-06.pdf
http://www.zdnet.com/big-data-as-a-service-is-here-but-is-anybody-ready-7000013257/
http://cmsreport.com/articles/big-data-as-a-service-has-arrived-5805
Source: OpenMind